Methodologies and Examples

To provide a starting point for institutions to estimate CECL, federal regulators initially hosted two webinars to show how CECL can be calculated within Excel:
- February 2018 Ask the Regulators webinar, "Practical Examples of How Smaller, Less Complex Community Banks Can Implement CECL." See presentation slides and a transcript of the remarks.
- April 2019 Ask the Regulators webinar “Weighted-Average Remaining Maturity (WARM) Method." See presentation slides and a transcript of the remarks.
The federal regulators presented commonly used methodologies in these webinars, but it is important to note that this does not indicate that these methods are "regulator preferred" or convey any kind of “safe harbor” status. There is no one method that is appropriate for every portfolio.
The three of the most commonly used methodologies are:
- Snapshot/Open Pool
- Remaining Life/Weighted Average Remaining Maturity (WARM)
- Vintage
Click on this icon to download an Excel workbook that contains examples of the three methodologies presented in the webinars.
to download an Excel workbook that contains examples of the three methodologies presented in the webinars.
When reviewing these examples, we encourage you to refer to the webinar materials in order to capture the full scope of the narrative, discussions and directions.
A Brief Look at the Methodologies
Snapshot/Open Pool
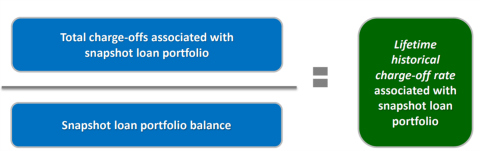
- The snapshot/open pool method takes a snapshot of a loan portfolio at a point in time in history and tracks that loan portfolio’s performance in the subsequent periods until its ultimate disposition.
- Charge-offs in the subsequent periods are aggregated to derive an unadjusted lifetime historical charge-off rate.
Remaining Life Method/Weighted Average Remaining Maturity (WARM)
- The Remaining Life Method uses average annual charge-off rates and the remaining life of the loan to estimate the allowance for credit losses.
- For amortizing assets, the remaining contractual life is adjusted by the expected scheduled payments and prepayments (i.e., pay downs)
- The average annual charge-off rate is applied to the amortization adjusted remaining life of the loan to determine the unadjusted lifetime historical charge-off rate.

Vintage
- “Vintage” refers to the year of origination.
- The Vintage Method tracks all charge-offs associated with a specific vintage (i.e., origination year).
- Borrowers’ historical charge-off patterns are used to estimate future losses.

- The Vintage Method tracks all charge-offs associated with a specific vintage (i.e., origination year).
- Borrowers’ historical charge-off patterns are used to estimate future losses.

.javascript:void(0);
